Hydroxyapatite has emerged as a material of exceptional interest across biomedical, dental, and orthopaedic applications in recent years. Its increasing popularity among hydroxyapatite manufacturers and powder suppliers is a testament to its unique bioactivity, biocompatibility, and structural similarity to human bone mineral. From hydroxyapatite nanoparticles to highly crystalline hydroxyapatite powder, its versatility continues to shape innovations in both medical research and clinical practice.
Hydroxyapatite is a naturally occurring mineral form of calcium apatite, with the chemical formula Ca₁₀(PO₄)₆(OH)₂. It is the primary inorganic component of human bone and teeth, accounting for approximately 60-70% of the bone’s dry weight. When people inquire, “What is hydroxyapatite made of?” or “What is calcium hydroxyapatite made from?”, the answer lies in its composition: a calcium phosphate compound engineered by nature for strength and resilience.
Its structure can occur in crystalline or nano-sized forms, and these hydroxyapatite crystals are known for their exceptional integration with biological tissues. In nanostructured form, hydroxyapatite nanoparticles offer even greater surface reactivity and are increasingly used in regenerative medicine.
Hydroxyapatite’s importance is rooted in its unparalleled biomimetic properties. Unlike synthetic polymers or foreign implants, hydroxyapatite is inherently recognizable by the body. It not only promotes osteoconduction (the support of bone growth on its surface) but also enhances osteointegration, facilitating seamless bonding between bone and implant materials.
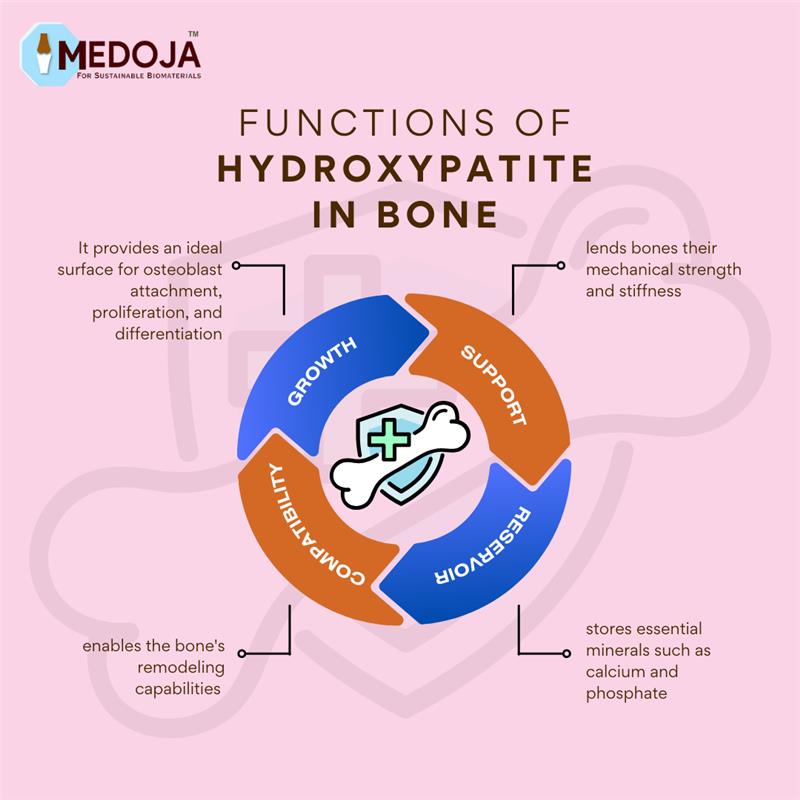
The functions of hydroxyapatite within bone are multifaceted and indispensable:
Beyond its role in the skeletal system, hydroxyapatite is gaining momentum in various cutting-edge fields:
So, Hydroxyapatite stands as a paragon of nature-inspired material science. Whether synthesized as fine powder, crystals, or nanoform, it continues to redefine the boundaries of biomedical engineering. As hydroxyapatite powder suppliers and research institutions push forward, the applications and innovations surrounding this remarkable biomaterial are poised for even greater expansion.